In primates the arm is adapted for precise positioning of the hand and thus assist in the hand's manipulative tasks. The ball and socket shoulder joint allows for movement of the arms in a wide circular plane, while the structure of the two forearm bones which can rotate around each other allows for additional range of motion at that level.
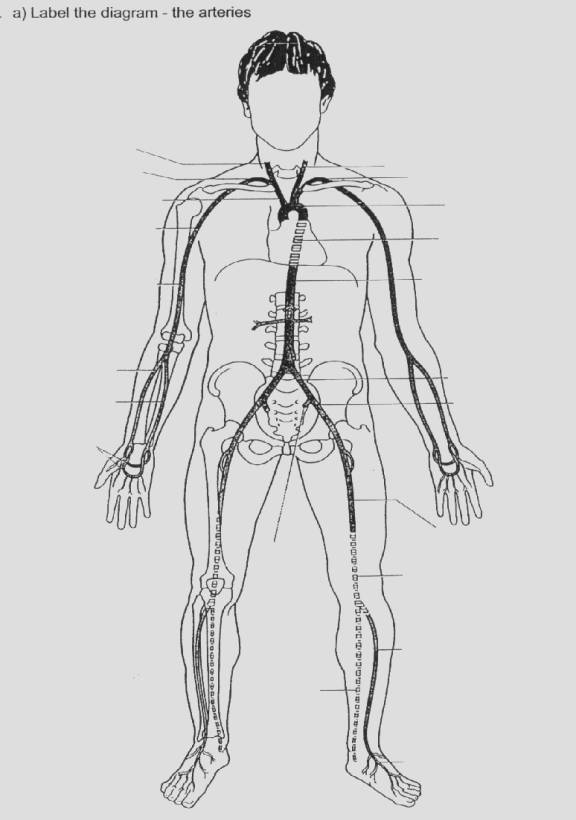
ARTERIES AND VEINS DIAGRAM
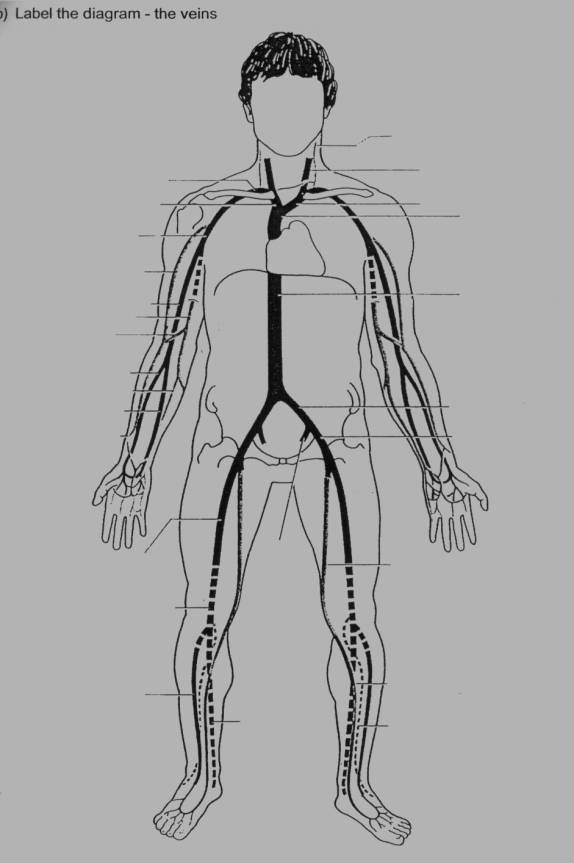
arteries and veins diagram
The humerus is the bone of the arm. It joins with the scapula above in the shoulder at the glenohumeral joint and with the ulna and radius below at the elbow. The elbow joint is the hinge joint between the distal end of the humerus and the proximal ends of the radius and ulna. The humerus cannot be broken easily. Its strength allows it to handle loading up to 300 pounds (140 kg).
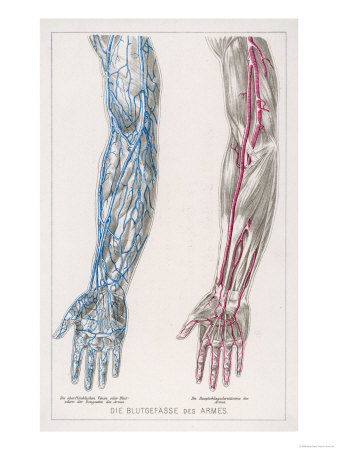
of arteries and veins in
The arm is divided by a fascial layer (known as lateral and medial intermuscular septa) separating the muscles into two osteofascial compartments: the anterior and the posterior compartments of the arm. The fascia merges with the periosteum (outer bone layer) of the humerus. The compartments contain muscles which are innervated by the same nerve and perform the same action.

each of these veins on an
The cubital fossa (colloquially known as the elbow pit) is clinically important for venepuncture and for blood pressure measurement.

arteries, veins,

and Veins Diagrams.
The musculocutaneous nerve, from C5, C6, C7, is the main supplier of muscles of the anterior compartment. It originates from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus of nerves. It pierces the coracobrachialis muscle and gives off branches to the muscle, as well as to brachialis and biceps brachii. It terminates as the anterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
of arteries and veins.
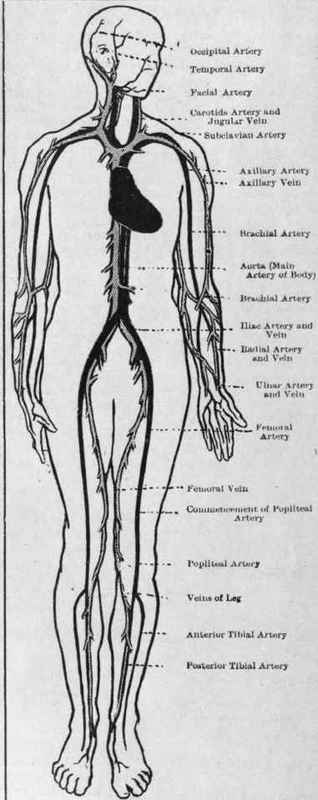
Chief arteries (dark) and

Veins. Share | | Email | Print
The radial nerve, which is from the fifth cervical spinal nerve to the first thoracic spinal nerve, originates as the continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. This nerve enters the lower triangular space (an imaginary space bounded by, amongst others, the shaft of the humerus and the triceps brachii) of the arm and lies deep to the triceps brachii. Here it travels with a deep artery of the arm (the profunda brachii), which sits in the radial groove of the humerus. This fact is very important clinically as a fracture of the bone at the shaft of the bone here can cause lesions or even transections in the nerve.
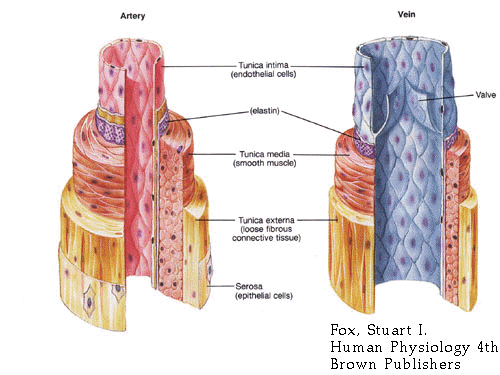
Arteries Vs. Veins Arteries:

Veins are able to carry three
The main artery in the arm is the brachial artery. This artery is a continuation of the axillary artery. The point at which the axillary becomes the brachial is distal to the lower border of teres major. The brachial artery gives off an important branch, the profunda brachii (deep artery of the arm). This branching occurs just below the lower border of teres major.

arteries and veins of the
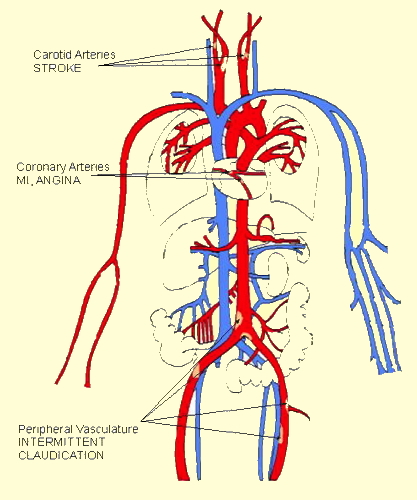
the coronary arteries,

Arteries and Veins

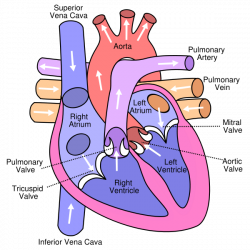
diagram of the heart
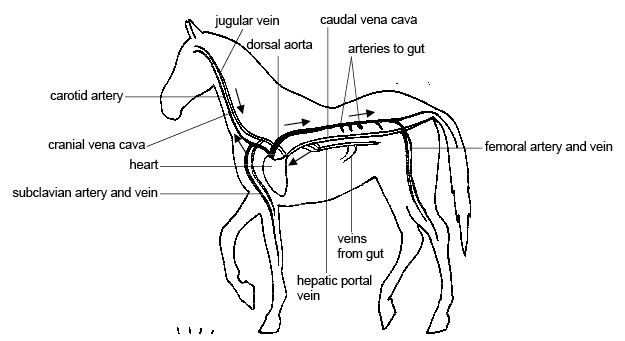
like arteries or veins.

ARTERIES AND VEINS DIAGRAM

arteries and veins diagram
The humerus is the bone of the arm. It joins with the scapula above in the shoulder at the glenohumeral joint and with the ulna and radius below at the elbow. The elbow joint is the hinge joint between the distal end of the humerus and the proximal ends of the radius and ulna. The humerus cannot be broken easily. Its strength allows it to handle loading up to 300 pounds (140 kg).

of arteries and veins in
The arm is divided by a fascial layer (known as lateral and medial intermuscular septa) separating the muscles into two osteofascial compartments: the anterior and the posterior compartments of the arm. The fascia merges with the periosteum (outer bone layer) of the humerus. The compartments contain muscles which are innervated by the same nerve and perform the same action.

each of these veins on an
The cubital fossa (colloquially known as the elbow pit) is clinically important for venepuncture and for blood pressure measurement.

arteries, veins,

and Veins Diagrams.
The musculocutaneous nerve, from C5, C6, C7, is the main supplier of muscles of the anterior compartment. It originates from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus of nerves. It pierces the coracobrachialis muscle and gives off branches to the muscle, as well as to brachialis and biceps brachii. It terminates as the anterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm.

of arteries and veins.

Chief arteries (dark) and

Veins. Share | | Email | Print
The radial nerve, which is from the fifth cervical spinal nerve to the first thoracic spinal nerve, originates as the continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. This nerve enters the lower triangular space (an imaginary space bounded by, amongst others, the shaft of the humerus and the triceps brachii) of the arm and lies deep to the triceps brachii. Here it travels with a deep artery of the arm (the profunda brachii), which sits in the radial groove of the humerus. This fact is very important clinically as a fracture of the bone at the shaft of the bone here can cause lesions or even transections in the nerve.

Arteries Vs. Veins Arteries:

Veins are able to carry three
The main artery in the arm is the brachial artery. This artery is a continuation of the axillary artery. The point at which the axillary becomes the brachial is distal to the lower border of teres major. The brachial artery gives off an important branch, the profunda brachii (deep artery of the arm). This branching occurs just below the lower border of teres major.

arteries and veins of the

the coronary arteries,

Arteries and Veins

diagram of the heart

like arteries or veins.
No comments:
Post a Comment